
Welcome to the fascinating world of smart building! What are the five smart building stages? In this article, we invite you on an exciting journey to explore the evolution of buildings – from traditional, manually controlled structures to the futuristic, fully autonomous buildings of tomorrow. We will not only showcase the defining features of a smart building but also delve into the various stages of development on the path to a fully autonomous structure.
Inhalt:
- Beyond the question of “what is a smart building?”
- Cost and energy efficiency
- User comfort and enhanced image
- Challenges and room for improvement
- Building digitalization: There is more than just black-and-white
- Smart buildings: Vision of the future or reality?
- The next steps
Imagine yourself as the protagonist of a captivating story, where you own a building and gradually transform it into a smart building. Along the way, you face challenges, make decisions, and discover how technology and data can enhance the efficiency, safety, and comfort of your building.
Beyond the question of “what is a smart building?”
Once upon a time, there was an ordinary building. It served its purpose, but it lacked that special something. The owner of the building, our protagonist, dreamed of transforming it into a smart building. However, he had no idea where to begin or what exactly makes a building smart.
One day, he came across this article and started learning more about the different stages of smart building development. He discovered the benefits of technology integration, data collection and analysis, and automation. With each step he took on this journey, his building became smarter and smarter.
A smart building, also known as an intelligent building, is more than just a building with some fancy gadgets. It’s a complex system that constantly evolves by integrating technology, data, and automation. However, not all smart buildings are created equal. In fact, there are various stages in the development of a smart building, ranging from manual buildings to fully autonomous ones.
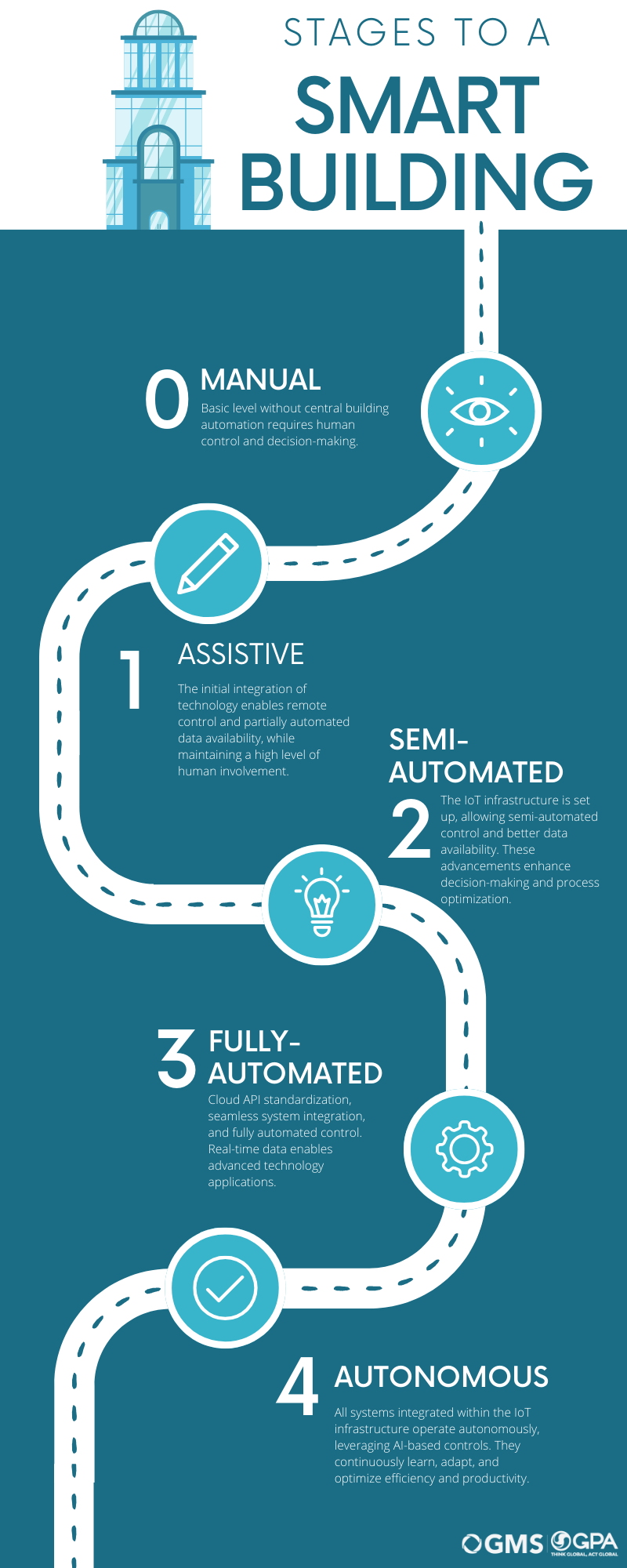
The rapid advancement of digitalization and technology in our world has greatly influenced how we design and utilize buildings. Smart buildings are no longer just a futuristic vision; they are now a reality. But what exactly defines a smart building? And what value do they offer compared to conventional buildings? To answer these questions, Deloitte, a leading consulting firm, conducted a comprehensive analysis. They evaluated and categorized 20 buildings into different smart building stages based on defined criteria.
Smart building stage 0: Manual buildings
The base stage of a smart building is actually not “smart” at all. At Stage 0 it is a manual building where all controls and data collection are done manually. There is no central building management system, and every action requires human intervention and decision-making. This building type can be considered the foundation or starting point for the transition toward a truly smart building.
Smart building stage 1: Assistive buildings
At Stage 1, we start to see the first signs of intelligence and technology integration. An assisted building has connected some trades to a central building management system, enabling remote control of the systems. Data is partially automated and available on demand. Although there is still a high degree of human involvement, these buildings are beginning to leverage the benefits of technology to make processes more efficient and improve the user experience.
Smart building stage 2: Semi-automated buildings
With Stage 2, we experience a significant increase in automation. In a partially automated building, there is an initial IoT infrastructure in place, and the technical building control is partially automated. Data is partially automated and available on demand. With the introduction of IoT devices, these buildings are becoming smarter and more efficient as they can collect and analyze data to make informed decisions and optimize processes.

Smart building stage 3: Fully automated buildings
Stage 3 is the fully automated building. Here, a standardized cloud API is available, and the systems are largely integrated into the IoT infrastructure. The building is controlled fully automatically, and data is available in real time. These buildings require minimal human intervention and can make many of their own decisions. They leverage advanced technologies like machine learning to detect patterns, make predictions, and adapt to changing conditions.
Smart building stage 4: Autonomous buildings
The final stage is the autonomous building. At stage 4, all systems are integrated into the IoT infrastructure. The building is autonomously controlled and AI-based. These buildings are not just “smart”. They learn and adapt to improve their efficiency and productivity constantly. They can respond to environmental changes and adjust accordingly to maximize comfort, safety, and energy efficiency.
Cost and energy efficiency
One of the key findings of the Deloitte report is that smart buildings are more cost-effective than conventional buildings. The operating costs of the analyzed smart buildings were, on average, up to 26% lower. Another major advantage is energy efficiency. The energy consumption of the analyzed smart buildings was, on average, 34% lower than that of conventional buildings. These savings are not only good for the managing budget but also for the environment.
User comfort and enhanced image
According to Deloitte, smart buildings also enhance user comfort in addition to cost and energy efficiency. Respondents confirmed experiencing a higher level of comfort in smart buildings, positively contributing to their image. These buildings signify innovation and progress, thus elevating the reputation of companies and organizations.
Challenges and room for improvement
Despite the numerous advantages, the Deloitte report highlights areas for improvement. Specifically, there is a need to enhance communication between users and providers. Variances exist in perceptions and expectations regarding topics such as cybersecurity, operational cost reduction, and CO2 reduction.
Furthermore, it is evident that users require support during periods of change. Many find the multitude of control options within user applications overly complex. Therefore, there is a demand for dialogue regarding the actual applications needed and assistance in their utilization.
Deloitte’s analysis demonstrates that smart buildings offer significant benefits but also present challenges. It is crucial to address these challenges and continuously work towards enhancing and advancing smart buildings. Only then can we fully harness these innovative structures’ potential and positively contribute to shaping our future.
Building digitalization: There is more than just black-and-white
This stage model helps us better understand the development of a smart building. It’s not just a question of “Is it a smart building or not?” but rather about at which stage of development it is. Each stage represents a step towards the ultimate goal: the autonomous building. It’s a continuous process driven by technological innovations and the increasing digitization of our world. Ultimately, the goal is to achieve the perfect smart building – a fully autonomous building at stage 4, capable of optimizing its resources, protecting and supporting its occupants, and positively impacting the environment.
Smart buildings: Vision of the future or reality?
A global study conducted by Deloitte in 2020 revealed a clear picture: 75% of surveyed executives from the commercial real estate sector agreed that smart buildings would become the new norm by 2025. Furthermore, 60% of the 750 global executives surveyed planned to significantly increase their investments in smart buildings in the short term (within 18 months).
Now, more than three years later, the global market is showing the first signs of this development. However, significant investments have not yet been made, and smart buildings have not become the new norm. So why haven’t smart buildings gained widespread adoption globally?
To answer this question, we must consider the current challenges. Rising energy costs, lower space utilization due to increased remote work, and emerging ESG regulations pose new challenges for the real estate sector. This question needs to be examined more closely, particularly in the context of existing buildings. When researching the benefits of smart buildings, clear facts and evidence are often lacking. Common market hypotheses persist, but hard facts often do not support them.
Nevertheless, progress in the field of smart buildings is undeniable. Following the flagship project “The EDGE” in Amsterdam in 2016, there was a noticeable hype for smart buildings in the real estate industry. In Germany, office buildings with an enhanced digital standard have already been constructed, such as “CUBE Berlin” (2020), the “Hammerbrooklyn. Digital Pavillon” in Hamburg (2021), and “OWP 12” in Stuttgart (2021), among others.
However, the question remains: When will smart buildings become the new norm globally, and how can we accelerate this process? It is clear that there is still much work ahead of us to make the benefits of smart buildings accessible to the broader market.
The next steps
So what about our story and our protagonist from the beginning of the article? After going through the different stages and transforming his building into a fully autonomous smart building, our smart building hero was finally able to unlock the full potential of his structure. He enhanced efficiency, improved resident comfort, and positively contributed to the environment.
That concludes our story, but it could be the beginning of your own. With the knowledge gained from this article, you are now ready to embark on your own journey into the world of smart buildings. Who knows, maybe your building will be the next autonomous milestone in the future of architecture.